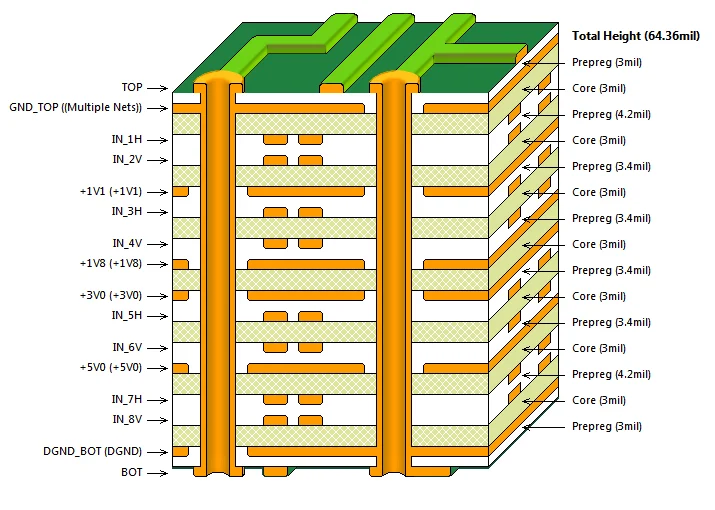
Based on the definition of the transmission line model outlined in the preceding article, transmission lines introduce the following effects into the overall circuit design:
- Reflected signals
- Delay and timing errors
- False switching
- Overshoot/Undershoot
- Induced Noise (or crosstalk)
- Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) radiation
1. Reflected Signals
If a trace is not properly terminated (impedance matched), signal pulses from the driving end are reflected at the receiving end. This induces unintended effects, distorting the signal profile. When distortion becomes severe, it can cause various errors leading to design failure. Simultaneously, the distorted signal becomes more susceptible to noise, further contributing to design failure. If these factors are inadequately addressed, EMI will significantly increase, impacting not only the design itself but potentially causing system-wide failure.
Primary causes of reflected signals: excessively long traces; unmatched termination of transmission lines; excessive capacitance or inductance; and impedance mismatch.
2. Delay and Timing Errors
Signal delay and timing errors manifest as signals failing to transition for a period while fluctuating between logic level thresholds. Excessive delay may cause timing errors and device malfunction.
Problems typically arise with multiple receivers. Circuit designers must determine worst-case delays to ensure design correctness. Causes of signal delay: driver overload, excessively long traces.
3. Multiple Logic Level Crossing Errors
Signals oscillating near logic level thresholds may repeatedly cross these boundaries, causing this error type. Multiple logic-level crossing errors represent a specific form of signal oscillation near logic thresholds, disrupting logic functionality. Causes of reflected signals: Excessively long traces, unterminated transmission lines, excessive capacitance or inductance, and impedance mismatch.
4. Overshoot and Undershoot
Overshoot and undershoot stem from either excessively long traces or overly rapid signal transitions. Although most components feature input protection diodes at their receiving ends, these overshoot levels can sometimes far exceed the component's power supply voltage range, causing damage.

5. Crosstalk
Crosstalk occurs when a signal transmitted on one line induces a related signal on an adjacent line on the PCB.
Crosstalk is reduced when signal lines are closer to ground planes and when line spacing is increased. Asynchronous signals and clock signals are more prone to crosstalk. Therefore, decoupling methods involve relocating the signal causing crosstalk or shielding the severely affected signal.
6. Electromagnetic Radiation
EMI (Electromagnetic Interference) encompasses issues related to excessive electromagnetic radiation and sensitivity to such radiation. EMI manifests when a digital system emits electromagnetic waves into its surroundings upon power-up, disrupting the normal operation of nearby electronic equipment. The primary causes are excessively high operating frequencies and improper layout/routing. While EMI simulation software exists, these tools are costly, and configuring simulation parameters and boundary conditions is challenging—directly impacting accuracy and practicality. The most common approach is to apply EMI control design rules at every stage, enabling rule-driven control throughout the design process.
Benchuang Electronics offers high-quality PCB layout and High-Speed PCB services. Contact us and send your specifications.