What are PCB Single-Sided Boards, PCB Double-Sided Boards and PCB Multilayer Boards
Printed circuit boards (PCBs) serve as the base for mounting electronic components and providing electrical connections between them. Structurally, PCBs are categorized into single-sided, double-sided, and multilayer boards.
Single-Sided PCB
A single-sided PCB is the most basic type, where components are concentrated on one side while conductive traces are concentrated on the other. Since traces appear only on one side, this PCB is termed single-sided. Due to stringent design constraints (traces cannot cross and must follow separate paths on a single side), single-sided PCBs are primarily used in legacy circuits.

Single-sided PCB layout primarily employs screen printing, where resist is applied to the copper surface. After etching, the solder mask is printed to mark components, followed by punching to create component vias and outlines. Additionally, photolithography using photosensitive resist is adopted for some low-volume, high-variety production.
Double-sided boards feature copper plating on both the Top (top layer) and Bottom (bottom layer). Both sides support routing and soldering, separated by an insulating layer. This is a commonly used PCB type. The ability to route traces on both sides significantly reduces routing complexity, leading to widespread adoption.

Both sides of a double-sided board carry traces, but to utilize traces on both sides, appropriate electrical connections between them are essential.
These “bridges” between circuits are called vias. Via holes are small holes in the PCB filled or plated with metal, enabling connections between traces on opposite sides. Since double-sided boards offer twice the area of single-sided boards, they overcome the routing challenges of single-sided boards (by allowing traces to cross over to the other side via holes), making them more suitable for more complex circuits than single-sided boards.
Multilayer PCB
PCB multilayer boards refer to multi-layer circuit boards used in electrical products. They incorporate multiple single- or double-sided wiring boards. A printed circuit board formed by alternating layers—such as one double-sided board as the inner layer with two single-sided boards as outer layers, or two double-sided boards as inner layers with two single-sided boards as outer layers—using a positioning system and insulating adhesive materials, with conductive patterns interconnected according to design specifications, becomes a four-layer or six-layer printed circuit board. These are also referred to as multilayer printed circuit boards. Common multilayer boards are typically 4-layer or 6-layer boards, while complex multilayer boards can reach dozens of layers.
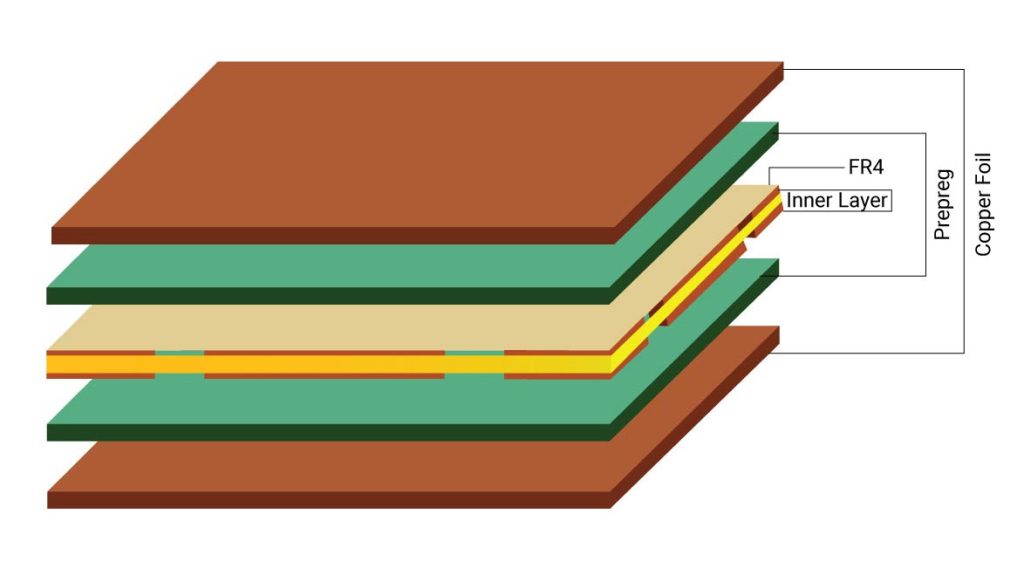
The primary difference between multilayer PCBs and single- or double-sided boards is the addition of internal power planes (maintaining internal power layers) and ground planes. Power and ground networks are primarily routed on the power planes. However, routing in multilayer boards primarily occurs on the top and bottom layers, with intermediate routing layers serving as supplementary paths. Consequently, multilayer board design follows methods similar to double-sided boards. The key lies in optimizing internal power layer routing to achieve a more rational circuit layout and superior electromagnetic compatibility.
BenChuang Electronics produces customized PCB boards. Contact us and send your specifications.


