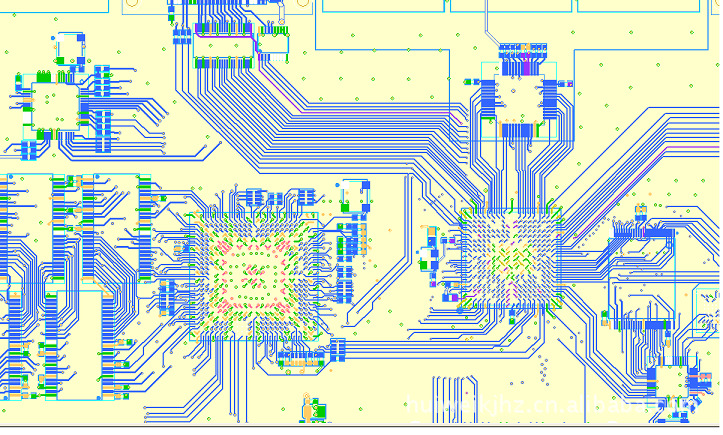
PCB
PCB is one of the most common components in electronic devices. It is typically made of non-conductive materials (usually paper, fiberglass, or plastic) with conductive traces formed on its surface to connect electronic components. PCB design can be done on a computer and produced during the manufacturing process. Designers convert circuit diagrams into physical layouts, then use CAD software to transmit them to manufacturers, who finally produce the PCBs through the manufacturing process.
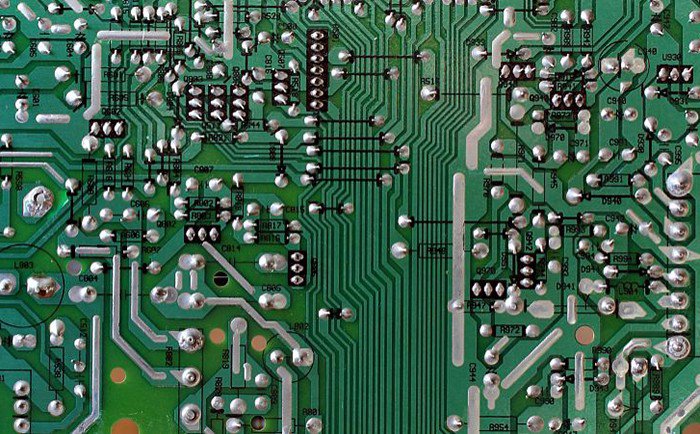
SMT
SMT is a technology that involves attaching components to the surface of a PCB. In traditional PCB manufacturing methods, components are typically connected to the circuit board using pins or soldered leads. However, SMT technology replaces traditional socket-mounted components with surface-mount devices (SMDs), allowing components to be directly attached to the surface of the PCB. This enhances component density, reliability, and manufacturing efficiency.
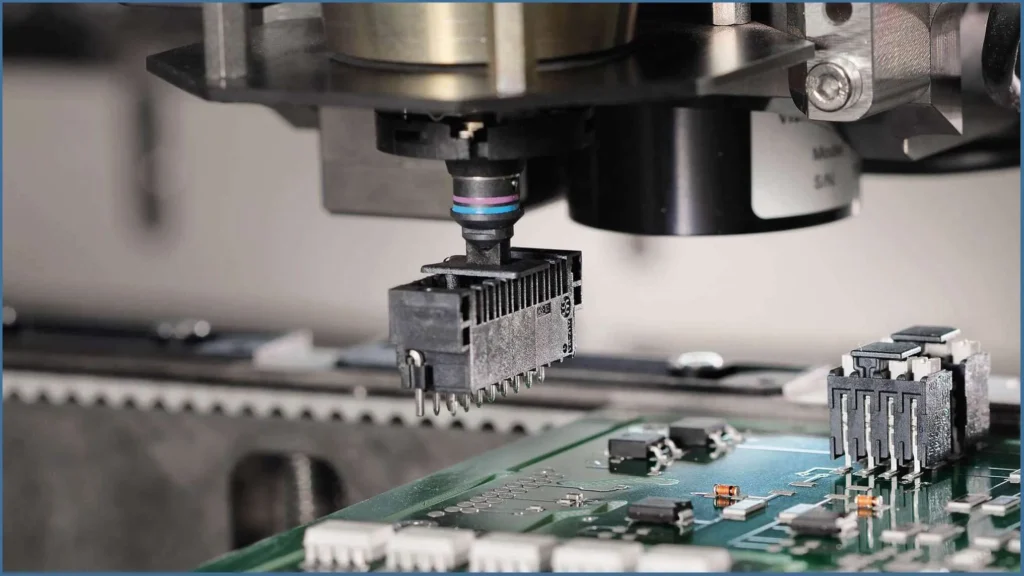
It is worth noting that while SMT technology reduces the use of through-hole components, certain special components (such as high-power components) may still require through-hole connections.
PCBA
PCBA refers to a PCB that has completed component placement and soldering. During the PCBA process, components are placed in their correct positions on the PCB using SMT equipment, then securely fixed to the PCB using hot air rework or other soldering methods. Ultimately, the PCBA is integrated into the final product as a finished component.
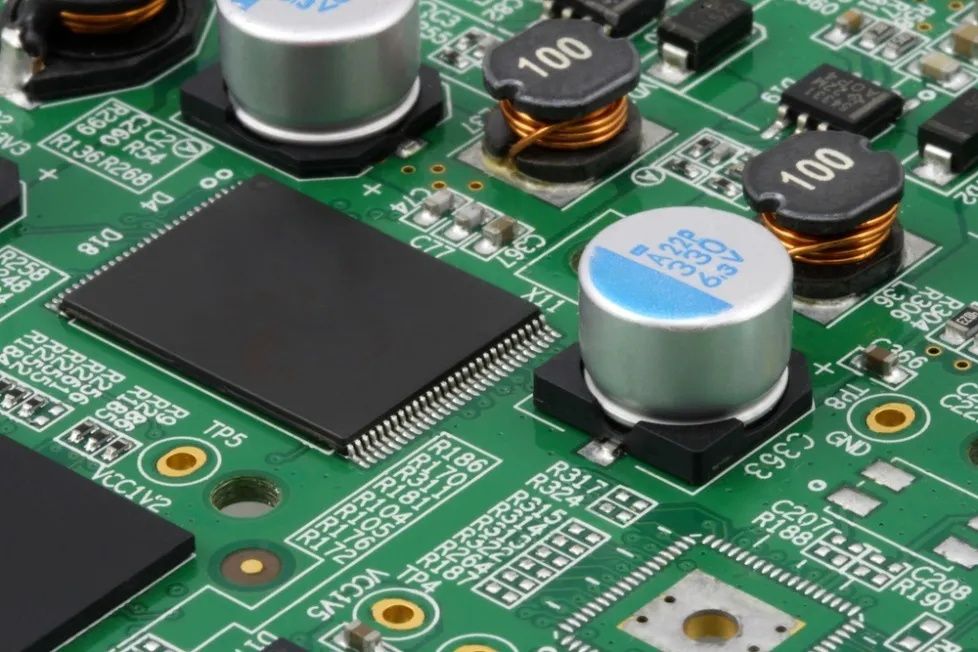
In summary, PCBs, SMT, and PCBA play distinct roles in the electronic manufacturing process. PCB serves as the foundation of the circuit board, facilitating connections between electronic components; SMT technology is a method for mounting surface-mount components onto a PCB, enabling components to be arranged more densely on the PCB, thereby enhancing circuit board performance and manufacturing efficiency; PCBA refers to a PCB that has completed component mounting and soldering, and after undergoing a series of tests and inspections, it can be directly integrated into the manufacturing of the final product.